Answer: The value of
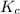 for given reaction is 0.465
for given reaction is 0.465
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Initial concentration of A = 0.650 M
Initial concentration of B = 1.35 M
Initial concentration of C = 0.300 M
Equilibrium concentration of A = 0.550 M
Equilibrium concentration of B = 0.400 M
For the given chemical equation:
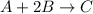
Initial: 0.65 1.35 0.30
At eqllm: 0.65-x 1.35-2x 0.30+x
Evaluating the value of 'x'
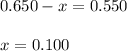
So, equilibrium concentration of B = 1.35 - 2x = [1.35 - 2(0.100)] = 1.15 M
Equilibrium concentration of C = (0.30 + x) = (0.300 + 0.100) = 0.400 M
The expression of
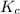 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![K_c=([C])/([A][B]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g5bwkf9na91ihaodz5p6nnrr0ds09r4p8o.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
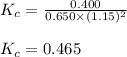
Hence, the value of
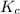 for given reaction is 0.465
for given reaction is 0.465