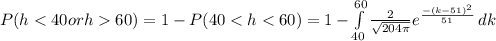Answer:
If n = 1000000, then
![P(h E [495000, 505000]) = \int\limits^(50500)_(495000) {(2)/(√(2000000\pi)) e^{(-(k-500000)^2)/(500000) }} \, dk](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/b4y98k8w830k43z8hpkmgyb8o9dijoo6af.png)
If n = 10400, then
![P(h E [495000, 505000]) = \int\limits^(50500)_(495000) {(2)/(√(2000000\pi)) e^{(-(k-500000)^2)/(500000) }} \, dk](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/b4y98k8w830k43z8hpkmgyb8o9dijoo6af.png)
If N = 102, then
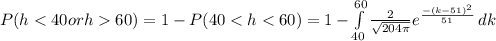
Explanation:
Since the coin is fair, then the probability that a filp is heads is 1/2. Given N tries, the amount of heads can be approximated with a Normal distribution with mean μ = N *1/2 = N/2 and standard deviation σ = √(N*1/2 * 1/2) = √N/ 2
The density function of that random variable is given by de following formula
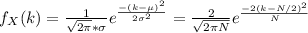
If n = 1000000, then
![P(h E [495000, 505000]) = \int\limits^(50500)_(495000) {(2)/(√(2000000\pi)) e^{(-(k-500000)^2)/(500000) }} \, dk](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/b4y98k8w830k43z8hpkmgyb8o9dijoo6af.png)
If n = 10400, then
![P(h E [495000, 505000]) = \int\limits^(50500)_(495000) {(2)/(√(2000000\pi)) e^{(-(k-500000)^2)/(500000) }} \, dk](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/b4y98k8w830k43z8hpkmgyb8o9dijoo6af.png)
If N = 102, then