Answer:
No, because either np or n(1 − p) are less than 15.
Explanation:
If a random variable X follows a Binomial distribution with parameters n and p and if n is large and p is small then the Normal approximation can be used to approximate the distribution of sample proportion
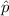 .
.
The conditions to be applied for Normal approximation are:
The random variable X can be defined as the number of students who are smokers.
Given:
n = 100
p = 0.04
Compute the value of np and n(1 - p) as follows:
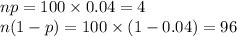
So n(1 - p) > 15 but np < 15.
Hence, the Normal approximation cannot be used to construct a confidence interval for the proportion of students in the population who are smokers.
The correct option is: No, because either np or n(1 − p) are less than 15.