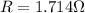Answer
given,
R₁= 4 Ω
R₂ = 3 Ω
When two resistors are connected in series
R = R₁ + R₂
R = 4 + 3
R = 7 Ω
When two resistors are connected in series then their effective resistance is equal to 7 Ω .
When two resistors are connected in parallel.
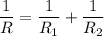
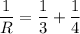
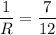
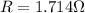
Hence, the equivanet resistance in parallel is equal to