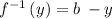Explanation:
Let f be a function having domain in the set X, and range in the set Y. Then f would be invertible if there exists a function g having domain Y and range X, such as:
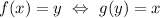
In other words, the function
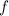 is applied to an input x, and gives an outcome of y, then its inverse function, let say
is applied to an input x, and gives an outcome of y, then its inverse function, let say
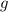 , can be applied to y to give the result of x.
, can be applied to y to give the result of x.
In other words,
y = f(x) if and only if x = g(y)
For example, considering the function
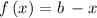
the inverse is: