Answer:
(a).The mass of the block of ice 87.16 kg.
(b). The distance is 24.98 m.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Horizontal force = 72.0 N
Distance = 12.5 m
Time = 5.50 s
We need to calculate the acceleration
Using equation of motion
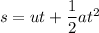
Where, u = initial velocity
a = acceleration
t = time
s = distance
Put the value into the formula
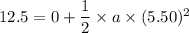
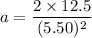
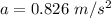
(a). We need to calculate the mass of the block of ice
Using formula of force
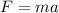
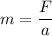
Put the value into the formula
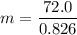
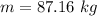
(b). If the worker stops pushing after 5.50 s.
We need to calculate the final velocity
Using equation of motion
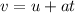
Put the value into the formula
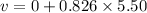
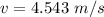
We need to calculate the distance
Using formula of velocity
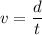
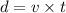
Put the value into the formula
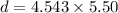
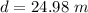
The distance is 24.98 m.
Hence, (a).The mass of the block of ice 87.16 kg.
(b). The distance is 24.98 m.