Answer:
1 mile
Step-by-step explanation:
We can use the following equation of motion to solve for this problem:
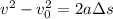
where v m/s is the final take-off velocity of the airplane,
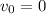 initial velocity of the can when it starts from rest, a is the acceleration of the airplanes, which are the same, and
initial velocity of the can when it starts from rest, a is the acceleration of the airplanes, which are the same, and
 is the distance traveled before takeoff, which is minimum runway length:
is the distance traveled before takeoff, which is minimum runway length:
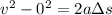
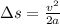
From here we can calculate the distance ratio
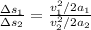
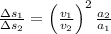
Since the 2nd airplane has the same acceleration but twice the velocity
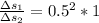
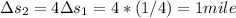
So the minimum runway length is 1 mile