Answer: The pH of resulting solution is 3.815
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles for given molarity, we use the equation:
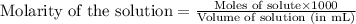
Molarity of lactic acid solution = 0.100 M
Volume of solution = 25.0 mL
Putting values in above equation, we get:
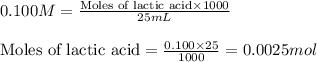
Molarity of NaOH solution = 0.050 M
Volume of solution = 23.5 mL
Putting values in above equation, we get:
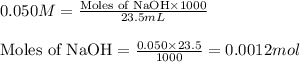
The chemical reaction for NaOH and lactic acid follows the equation:
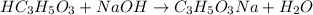
Initial: 0.0025 0.0012
Final: 0.0013 - 0.0012
Volume of solution = 25 + 23.5 = 48.5 mL = 0.0485 L (Conversion factor: 1 L = 1000 mL)
To calculate the pH of acidic buffer, we use the equation given by Henderson Hasselbalch:
![pH=pK_a+\log(([salt])/([acid]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/biology/college/6usxe642bp3w274zbcv30her0kcessu95f.png)
![pH=pK_a+\log(([C_3H_5O_3Na])/([HC_3H_5O_3]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/o1ytsd4upqsad6wj4bkm7shg6y2vj1c3fr.png)
We are given:
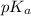 = negative logarithm of acid dissociation constant of lactic acid = 3.85
= negative logarithm of acid dissociation constant of lactic acid = 3.85
![[HC_3H_5O_3]=(0.0013)/(0.0485)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/w9vau8e9931qvk9xhnl883i2r24nm5ynzd.png)
![[C_3H_5O_3Na]=(0.0012)/(0.0485)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/urz0gpg3ipc3ysp5if0styr99m90fnme62.png)
pH = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
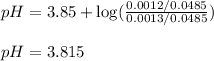
Hence, the pH of resulting solution is 3.815