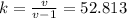Answer:
1) o=1.18 kg/m^3; r=286.987 J/(kg K); 2) T=871.12 K, U=375 kJ; 3) cp=438.793 J/(kg K), cv=430.480 J/(kg K), v=1.0.193, k=52.8135
Step-by-step explanation:
1)
This questions is fully based on the Ideal Gas Law:
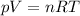
As we need to find initial density, we should change temperature to Kelvins:
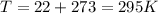
In addition, we should re-calculate amount of substance n, using mass m and MWair:
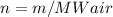
As it is known, density can be calculated, as:
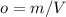
Now, we can use all equations in the ideal gas law:
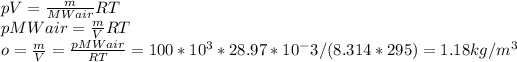
To calculate specific gas constant for the given scenario (r), we should do the following:
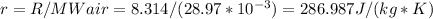
Note, that we converted MWair to kg/mol using (10^(-3)).
2)
To solve this question, we should use again ideal gas law, from where we can directly find temperature of the gas:

Note, that all values were converted to SI units for the calculations (1 bar= 10^5 Pa).
To find internal energy, we can use the following equation:
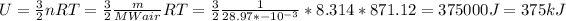
3)
To find specific heat, we can use the following ideal gas laws:
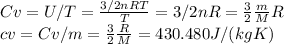
Then, the cp, can be calculated using cv and R:
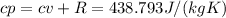
The thermal coefficient v represents the ratio between cp and cv:
v=cp/cv=1.0193
Finally, we can find k: