Answer:
In case of 5 m/s:
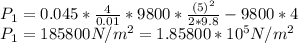
 >
>
 i.e
i.e
 >0, It means Water will leak out of hole.
>0, It means Water will leak out of hole.
In case of 0.5 m/s:
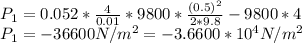
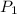 <
<
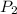 i.e
i.e
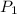 <0. It means air will enter into the pipe.
<0. It means air will enter into the pipe.
Step-by-step explanation:
Note:
Values of constant v,f and
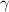 can vary according to the conditions. Value taken below are taken from water properties table.
can vary according to the conditions. Value taken below are taken from water properties table.
According to Bernoulli Equation: Considering the frictional affects
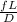
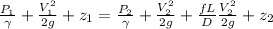
Where:
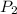 is the pressure at other end of pipe(outlet)=0
is the pressure at other end of pipe(outlet)=0
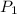 is the pressure at hole
is the pressure at hole
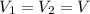
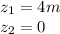
Above equation will become:
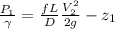
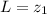
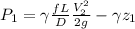
Calculating Re number:
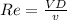
Where:
V is the velocity
D is the diameter
v is the kinematic viscosity of water. Lets consider it
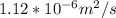 . However kinematic viscosity can be taken according to temperature.
. However kinematic viscosity can be taken according to temperature.
In case of 5 m/s:
Re=
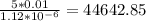
For galvanized iron pipe , Roughness coefficient ε is 0.15 mm
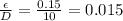
From Moody Charts, At above Re and
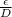 , Value of friction coefficient f is≈0.045.
, Value of friction coefficient f is≈0.045.
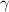 ≈9800 N/m^2
≈9800 N/m^2
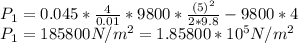
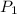 >
>
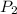 i.e
i.e
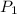 >0, It means Water will leak out of hole.
>0, It means Water will leak out of hole.
In case of 0.5 m/s:
Same above Procedure:
Calculating Re:
Re=
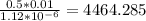
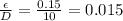
From Moody Charts, At above Re and
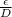 , Value of friction coefficient f is≈0.052.
, Value of friction coefficient f is≈0.052.
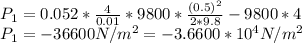
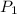 <
<
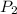 i.e
i.e
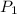 <0. It means air will enter into the pipe.
<0. It means air will enter into the pipe.