Answer:
Initial Kinetic energy of alpha particle is 9.45x10⁻¹³ J .
Step-by-step explanation:
The distance at which the initial kinetic energy of the particle is equal to the potential energy is known as closest distance. As it is Rutherford scattering, so it is a coulomb potential energy.
Let K be the initial kinetic energy of alpha particle and r be the closest approach distance. So,
Initial Kinetic Energy = Coulomb Potential Energy
K =
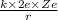
Here, k is constant, e is charge of electron and Z is the atomic number of silver.
Put 9x10⁹ N m²/C² for k, 1.6x10⁻¹⁹ C for e, 47 for Z and 22.9x10⁻¹⁵ m for r in the above equation.
K =
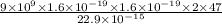
K = 9.45x10⁻¹³ J