Answer:
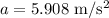
Step-by-step explanation:
To get the magnitude of the acceleration you need to find the change in velocity across the nozzle. To do that you can use the continuity equation which stated that the flow rate is the same in every point in the flow. So in this case you define the points at the nozzle inlet and at the nozzle outlet:
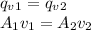
To get the velocity at point 1 you can just divide the flow rate by the surface:
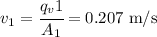
Now the expression for the velocity at point 2 is:
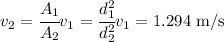
Now if you assume linear change of velocity across the nozzle you can use the following expression for the acceleration:
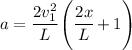
where L is your nozzle length (20 cm).
This equation depends on the position of your particle moving down the centerline of the nozzle. I sketched it: