Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Mass of copper calorimeter, (
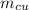 ) = 0.1 kg
) = 0.1 kg
specific heat of copper calorimeter, (
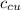 ) = 390 J/kg K
) = 390 J/kg K
mass of water, (
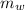 ) = 0.160 kg
) = 0.160 kg
specific heat of water, (
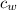 ) = 4190 J/kg K
) = 4190 J/kg K
mass of ice, (
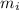 ) = 0.018 kg
) = 0.018 kg
latent heat of ice =
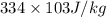
mass of lead, (
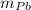 ) = 0.75 kg
) = 0.75 kg
specific heat of lead, (
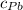 ) = 130 J/kg K
) = 130 J/kg K
Heat lost by the lead is
Q =
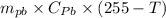
=
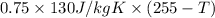
= 97.5 (255 - T)
Now, heat gained by calorimeter is calculated as follows.
Q =
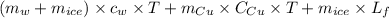
=
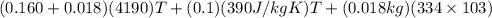
Hence, heat loss by lead is equal to heat gained by calorimeter .
So, 97.5 (255 - T ) = 745.82 T + 39 T + 6012
18850.5 = 882.32 T
T =
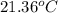
Thus, we can conclude that the value of final temperature is
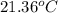 .
.