Answer:
0.2 kcal/mol is the value of
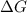 for this reaction.
for this reaction.
Step-by-step explanation:
The formula used for is:
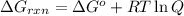
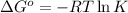
where,
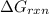 = Gibbs free energy for the reaction
= Gibbs free energy for the reaction
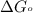 = standard Gibbs free energy
= standard Gibbs free energy
R =Universal gas constant
T = temperature
Q = reaction quotient
k = Equilibrium constant
We have :
Reaction quotient of the reaction = Q = 46
Equilibrium constant of reaction = K = 35
Temperature of reaction = T = 25°C = 25 + 273 K = 298 K
R = 1.987 cal/K mol
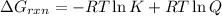
![=-1.987 cal/K mol* 298 K\ln [35]+1.987 cal/K mol* 298K* \ln [46]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/engineering/college/sfnorpfohkxdvc7jh5zvewmo1wexckc29r.png)
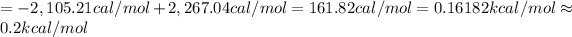
1 cal = 0.001 kcal
0.2 kcal/mol is the value of
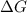 for this reaction.
for this reaction.