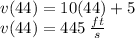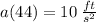Answer:
The velocity function is
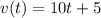 .
.
The acceleration function is
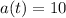 .
.
When t = 44, the velocity is
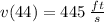 .
.
When t = 44, the acceleration is
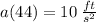 .
.
Explanation:
We know that the position function is given by
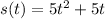
Velocity is defined as the rate of change of position or the rate of displacement. If you take the derivative of the position function you get the instantaneous velocity function.
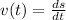
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity. If you take the derivative of the instantaneous velocity function you get the instantaneous acceleration function.
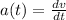
The instantaneous velocity function is given by
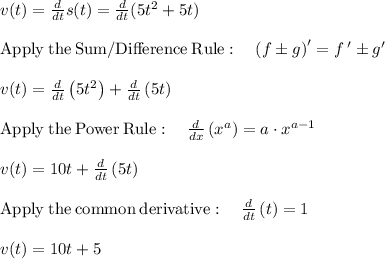
The instantaneous acceleration function is given by
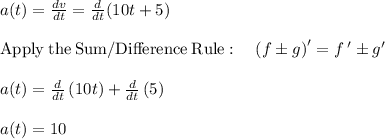
To find the velocity and acceleration when t = 44, we substitute this value into the velocity and acceleration functions