Answer:
The correct answer is
The maximum speed of free fall for the sky diver is 52.41 m/s
and the speed reached after 100 m is 37.44 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
From Force = mass × acceleration
Aerodynamic drag force = FD = k·V², where k = 0.25 N·s²/m²
The maximum speed, v, of free fall where m·a = 0 at terminal velocity
Mass × Gravity - Aerodynamic drag force = ma = 0
∴ 70 kg × 9.81 m/s² - 0.25 N·s²/m²× v² =0
Therefore v = 52.41 m/s
The speed after 100 m of free fall is given by
V =
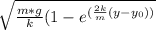
Substituting we have, where y - y₀ = 100 then v = 37.44 m/s
b) To plot the relation we have
Speed to time relation as v or s(t) =
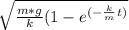
Where S(t) is he speed at time t
and the relation between time and distance = v × t
Please see the attached graphs