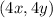Answer: OPTION A.
Explanation:
Dilation is defined as transformations in which the Image (The figure obtained after the transformation) and the Pre-Image (The original figure) have the same shape, but their sizes are different.
For a dilation using a scale factor "k" and centered at the origin, the rule is:
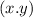 →
→
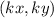
Let's pick the point S of the Pre-Image RSTU. This is :
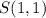
And the point S' of the Image R'S'T'U' is:
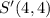
You can identify that the coordinates of S' are obtained by multiplying the coordinates of the point S by this scale factor:
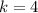
Therefore, the rule that yields this dilation is:
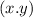 →
→