Answer:
There is not enough evidence to support the claim that interested consumers would be willing, on average, to pay $20.00 for the product.
Explanation:
We are given the following in the question:
Population mean, μ = $20.00
Sample mean,
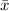 = $18.14
= $18.14
Sample size, n = 315
Population standard deviation, σ = $2.98
a) Reference value
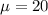
b) First, we design the null and the alternate hypothesis
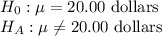
We use Two-tailed z test to perform this hypothesis.
Formula:
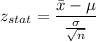
Putting all the values, we have
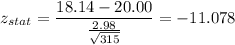
c) Calculating the p-value at 5% significance level
P-Value < 0.00001
Thus,
p<0.001
d) Calculating the p-value at 1% level of significance
P-Value < 0.00001
Thus,
p<0.001
Thus, at both 5% and 1% level of significance, the p value is lower than the significance level, we fail to accept the null hypothesis and reject it.
There is not enough evidence to support the claim that interested consumers would be willing, on average, to pay $20.00 for the product.