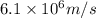Answer : The velocity of an electron is,
Explanation :
According to de-Broglie, the expression for wavelength is,
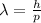
and,
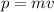
where,
p = momentum, m = mass, v = velocity
So, the formula will be:
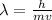 .............(1)
.............(1)
where,
h = Planck's constant =
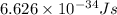
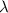 = wavelength =
= wavelength =
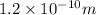
m = mass of electron =
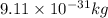
v = velocity of electron = ?
Now put all the given values in formula 1, we get:
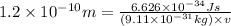
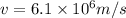
Thus, the velocity of an electron is,