Step-by-step explanation:
Formula to calculate work done by motor is as follows.
Work done by motor =
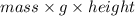
where, g = gravitational constant = 10
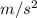
Therefore, work done by motor is as follows.
Work done by motor =
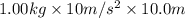
= 100.0 J
Now, heat lost by water will be calculated as follows.
q =

=
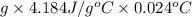
= 10.0 J
Hence, heat gained by motor = heat lost by water
As, heat gained by motor = 10.0 J
So, change in energy = heat gained - work done
Therefore, change in energy will be calculated as follows.
Change in energy = heat gained - work done
= (10.0 J) - (100.0 J)
= -90.0 J
Thus, we can conclude that change in the energy of the battery contents is -90.0 J.