Answer:
Part a: The equation is a linear first order differential equation as superposition and homogeneity is satisfied.
Part b: The solution of the differential equation is
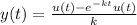
Step-by-step explanation:
Part a:
Let us suppose the differential equation is given as
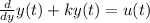
For a solution, it is given as
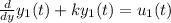
For another solution it is given as
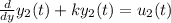
Adding these two solution gives
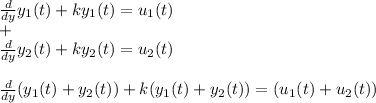
Which is also the solution of the equation and thus as superposition (additivity) and homogeneity is satisfied, so the equation is a linear first order differential equation.
Part b
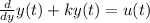
So taking Laplace on both sides
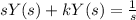
Here
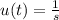
Rearranging the equation gives
![Y(s)=(1)/(k(s+k))\\Y(s)=(1)/(k)[(1)/(s)-(1)/(s+k)]\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/wz0hhp85qj2q0jzpxyle93vutxkchdej46.png)
Taking inverse Laplace gives
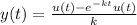
This is the solution of the differential equation.