Answer:
The pressure of the gas is:
Doubled
Step-by-step explanation:
Byole's Law = Pressure of fixed amount of gas is inversely proportional to Volume at constant temperature.
PV = k = constant
P1V1 = P2V2
Charle's Law: The volume of ideal gas at fixed pressure is directly proportional to Pressure.
V/T = constant
V1/T1 = V2/T2
On combinig the charles and byole's law , we get:
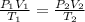
Now , According to question :
V2 = V1
T2 = 2(T1)
We have to find the relation between the pressure :
insert the value in the equation
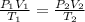
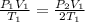
V1 and V1 & T1 and T1 cancels each other,
So we get
P2 = 2 P1
So the new pressure is double of the original pressure