Answer:
No,
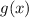 and
and
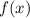 are not inverses of each other.
are not inverses of each other.
Explanation:
Given functions:
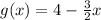
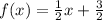
To tell whether
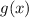 and
and
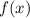 are inverse of each other.
are inverse of each other.
Solution:
If
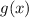 and
and
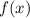 are inverse of each other, then:
are inverse of each other, then:
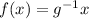 or
or
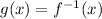
Thus, to check if they are inverse of each other, we will find inverse of function
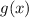 and see if it is =
and see if it is =
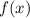
We have:
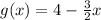
In order to find inverse we will replace
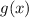 with
with
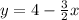
Then we switch
 and
and
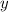
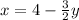
Then, we solve for
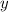
Subtracting both sides by 4.
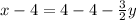
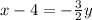
Multiplying both sides by 2.
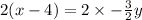
Using distribution:
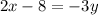
Dividing both sides by -3.
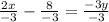
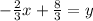
Thus inverse of function
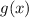 can be given as:
can be given as:
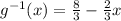
Since
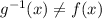 , hence they are not inverse functions of each other.
, hence they are not inverse functions of each other.