Answer:
4.1x10⁻⁵
Step-by-step explanation:
The dissociation of an acid is a reversible reaction, and, because of that, it has an equilibrium constant, Ka. For a generic acid (HA), the dissociation happens by:
HA ⇄ H⁺ + A⁻
So, if x moles of the acid dissociates, x moles of H⁺ and x moles of A⁻ is formed. the percent of dissociation of the acid is:
% = (dissociated/total)*100%
4.4% = (x/[HA])*100%
But x = [A⁻], so:
[A⁻]/[HA] = 0.044
The pH of the acid can be calcualted by the Handersson-Halsebach equation:
pH = pKa + log[A⁻]/[HA]
3.03 = pKa + log 0.044
pKa = 3.03 - log 0.044
pKa = 4.39
pKa = -logKa
logKa = -pKa
Ka =
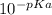
Ka =
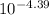
Ka = 4.1x10⁻⁵