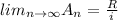Answer:
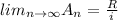
Explanation:
For this case we have this expression:
![A_n = R [(1 -(1+i)^(-n))/(i)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/dew0oj3zx7upp51g42i79wwb8lmxtqto1g.png)
The lump sum investment of An is needed to result in n periodic payments of R when the interest rate per period is i.
And we want to find the:
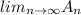
So we have this:
![lim_(n \to \infty) A_n = lim_(n \to \infty)R [(1 -(1+i)^(-n))/(i)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/l3lnqrj3gngfsulxqtfza68i184cvft2lk.png)
Then we can do this:
![lim_(n \to \infty) A_n = lim_(n \to \infty) R [(1 -(1)/((1+i)^n))/(i)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/2e0myrd332f4yianclqicf01yhfjj6xk6a.png)
![lim_(n \to \infty) A_n = R lim_(n \to \infty) [(1 -(1)/((1+i)^n))/(i)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/qej7m3v3n7mn780xw40d4ta72bv0h3cclx.png)
And after find the limit we got:
![lim_(n \to \infty) A_n = R [(1-0)/(i)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/rvef2y5dbjscvcmxpkxy8xlzeypa3lkz29.png)
Becuase :
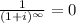
And then finally we have this: