This is an incomplete question, here is a complete question.
A 19.2 g quantity of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) is allowed to sublime (evaporate) in an apparatus. Calculate the expansion work done against a constant external pressure of 0.995 atm and at a constant temperature of 22 degrees C. Assume that the initial volume of dry ice is negligible and that CO₂ behaves like an ideal gas.
Answer : The expansion work done is, -1058.33 J
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the volume of gas.
Using ideal gas equation:
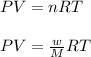
where,
P = pressure of gas = 0.995 atm
Conversion used : (1 atm = 760 torr)
V = volume of gas = ?
T = temperature of gas =
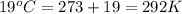
R = gas constant = 0.0821 L.atm/mole.K
w = mass of gas = 19.2 g
M = molar mass of carbon dioxide gas = 44 g/mole
Now put all the given values in the ideal gas equation, we get:
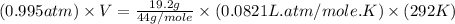
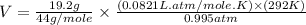
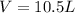
Now we have to calculate the work done.
Formula used :
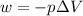
where,
w = work done
p = pressure of the gas = 0.995 atm
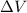 = volume = 10.5 L
= volume = 10.5 L
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
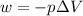
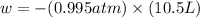
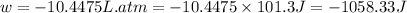
conversion used : (1 L.atm = 101.3 J)
Thus, the expansion work done is, -1058.33 J