Answer: The percent by mass of ethylene in the equilibrium gas mixture is 3.76 %
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Initial partial pressure or ethane = 24.0 atm
The chemical equation for the dehydration of ethane follows:
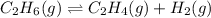
Initial: 24.0
At eqllm: 24-x x x
The expression of
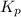 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
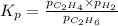
We are given:
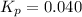
Putting values in above expression, we get:
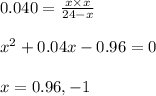
Neglecting the value of x = -1 because partial pressure cannot be negative.
So, partial pressure of hydrogen gas at equilibrium = x = 0.96 atm
Partial pressure of ethylene gas at equilibrium = x = 0.96 atm
Partial pressure of ethane gas at equilibrium = (24-x) = (24 - 0.96) atm = 23.04 atm
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation given by ideal gas, which follows:
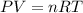 .........(1)
.........(1)
To calculate the mass of a substance, we use the equation:
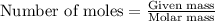 ..........(2)
..........(2)
We are given:
![P=23.04atm\\V=30.0L\\T=800^oC=[800+273]K=1073K\\R=0.0821\text{ L. atm }mol^(-1)K^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/15t3k9qxiwvn5esu7m12w0i3fx07dqthbc.png)
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
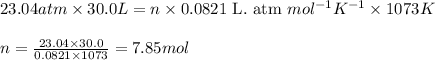
We know that:
Molar mass of ethane gas = 30 g/mol
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
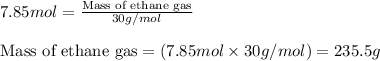
We are given:
![P=0.96atm\\V=30.0L\\T=800^oC=[800+273]K=1073K\\R=0.0821\text{ L. atm }mol^(-1)K^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zlygn0jdroy4h4gzn71z3zoab354615v3j.png)
Putting values in equation 1, we get:

We know that:
Molar mass of ethylene gas = 28 g/mol
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
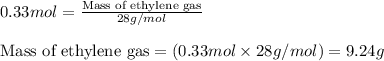
We are given:
![P=0.96atm\\V=30.0L\\T=800^oC=[800+273]K=1073K\\R=0.0821\text{ L. atm }mol^(-1)K^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zlygn0jdroy4h4gzn71z3zoab354615v3j.png)
Putting values in equation 1, we get:

We know that:
Molar mass of hydrogen gas = 2 g/mol
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
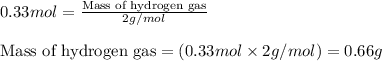
To calculate the mass percentage of ethylene in equilibrium gas mixture, we use the equation:
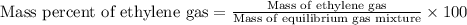
Mass of equilibrium gas mixture = [235.5 + 9.24 + 0.66] = 245.4 g
Mass of ethylene gas = 9.24 g
Putting values in above equation, we get:
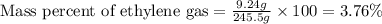
Hence, the percent by mass of ethylene in the equilibrium gas mixture is 3.76 %