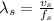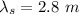Answer:
a)
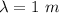
b)
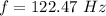
c)
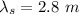
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
distance between the fixed end of strings,
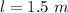
mass of string,
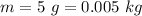
tension in the string,
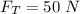
a)
Since the wave vibrating in the string is in third harmonic:
Therefore wavelength λ of the string:
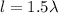
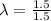
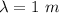
b)
We know that the velocity of the wave in this case is given by:
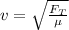
where:
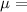 linear mass density
linear mass density
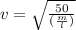
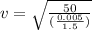
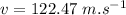
Now, frequency:
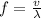
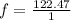
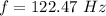
c)
When the vibrations produce the sound of the same frequency:
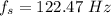
Velocity of sound in air:
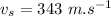
Wavelength of the sound waves in air: