Answer:
The momentum of the particle at the end of the 0.13 s time interval is 7.12 kg m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The momentum of the particle is related to force by the following equation:
Δp = F · Δt
Where:
Δp = change in momentum = final momentum - initial momentum
F = constant force.
Δt = time interval.
Let´s calculate the x-component of the momentum after the 0.13 s:
final momentum - 8 kg m/s = -7 N · 0.13 s
final momentum = -7 kg m/s² · 0.13 s + 8 kg m/s
final momentum = 7.09 kg m/s
Now let´s calculate the y-component of the momentum vector after the 0.13 s. Since the particle wasn´t moving in the y-direction, the initial momentum in this direction is zero:
final momentum = 5 kg m/s² · 0.13 s
final momentum = 0.65 kg m/s
Then, the mometum vector will be as follows:
p = (7.09 kg m/s, 0.65 kg m/s)
The magnitude of this vector is calculated as follows:
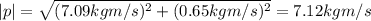
The momentum of the particle at the end of the 0.13 s time interval is 7.12 kg m/s