Answer:
5.0x10⁻⁵ M
Step-by-step explanation:
It seems the question is incomplete, however this is the data that has been found in a web search:
" One way the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) tests for chloride contaminants in water is by titrating a sample of silver nitrate solution. Any chloride anions in solution will combine with the silver cations to produce bright white silver chloride precipitate. Suppose a EPA chemist tests a 250 mL sample of groundwater known to be contaminated with nickel(II) chloride, which would react with silver nitrate solution like this:
NiCl₂ + 2AgNO₃ → 2AgCl + Ni(NO₃)₂
The chemist adds 50 mM silver nitrate solution to the sample until silver chloride stops forming. She then washes, dries, and weighs the precipitate. She finds she has collected 3.6 mg of silver chloride. Calculate the concentration of nickel(II) chloride contaminant in the original groundwater sample. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. "
Keep in mind that while the process is the same, if the values in your question are different, then your answer will be different as well.
First we calculate the moles of nickel chloride found in the 250 mL sample:
- 3.6 mg AgCl ÷ 143.32 mg/mmol *
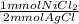 = 0.0126 mmol NiCl₂
= 0.0126 mmol NiCl₂
Now we divide the moles by the volume to calculate the molarity:
- 0.0126 mmol / 250 mL = 5.0x10⁻⁵M