Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction equation will be as follows.
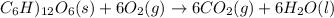
It is given that the total energy liberated is -2810 kJ/mol. As the sign is negative this means that energy is being released. Also, it is given that the energy required to synthesis is -64.1 kJ/mol.
Therefore, calculate the number of moles of compound as follows.
No. of moles =
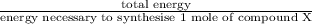
=
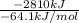
= 43.83 mol
= 44 mol (approx)
Thus, we can conclude that the number of moles of compound is 44 mol.