Answer:
the electric field is zero and the potential is positive.
Step-by-step explanation:
Electric field being a vector quantity results zero at a halfway between the two identical positive charges.
- As we know the electric field lines emerge outward from a positive charge, so here in the mid-way of the charges the field lines oppose each other and cancel out.
Mathematically electric field is given as:
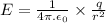
where:
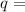 charge due to which electric field is present.
charge due to which electric field is present.
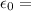 permittivity of free space
permittivity of free space
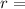 distance of observation of the electric field from the charge producing it.
distance of observation of the electric field from the charge producing it.
- Whereas, electric potential is a scalar quantity defined as the the work done to bring that charge from its initial point to the concerned point. It always adds up.
Mathematically:
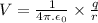
where:
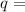 charge due to which electric potential is present.
charge due to which electric potential is present.
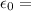 permittivity of free space
permittivity of free space
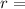 distance of observation of the electric potential from the charge producing it.
distance of observation of the electric potential from the charge producing it.