Step-by-step explanation:
Let us proceed with a reaction
A(aq)+B(aq)
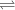 C(aq) + D(g)
C(aq) + D(g)
Taking A, B and C are in aqueous solution. D being a gas. The reaction is carried out in a close vessel. As reaction proceeds, A and B react to give C and D. As the concentration of C and D increases, they react to give back A and B. Now suppose the reaction is carried out in a open vessel so that the gas D can escape in the atmosphere. So the gas D is no longer available to react with C. So reverse reaction will not occur. The forward reaction is forced to reach 100 %
Let us take another example.
A(aq)+B(aq)
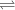 C(aq) + D(aq)
C(aq) + D(aq)
Here, D is a volatile liquid. As soon as D is formed, it is removed by distillation. So D is no longer available to react with C. So reverse reaction will not occur. The forward reaction is forced to reach 100 %