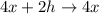Answer:
a)
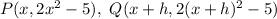
b)
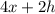
c)
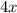
Explanation:
Given the curve
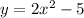
a) If the x-coordinate of P is
 , then the y-coordinate is
, then the y-coordinate is
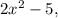 so point P has coordinates
so point P has coordinates
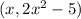
If the x-coordinate of Q is
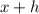 , then the y-coordinate is
, then the y-coordinate is
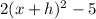 so point Q has coordinates
so point Q has coordinates
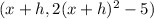
b) The gradient of the secant RQ is
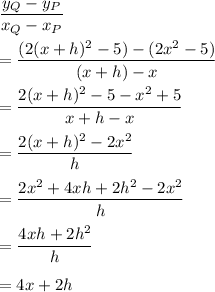
c) If
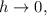 then the gradient
then the gradient