To solve this problem we will take the concept given by the frictional force, which warns that it is the product between the normal force (mg) by the static friction coefficient. In turn, this value of the coefficient will be taken as 1/2 to facilitate calculations (and not 1 2, as it appears in the problem, perhaps due to the omission of the division symbol).
Thus, the maximum frictional force that can be applied on the block before it is in motion will be given by the function,
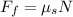
Where,
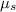 = Coefficient of static friction
= Coefficient of static friction
N = Normal Force
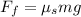
Replacing the values we have that,
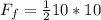
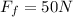
Therefore the magnitude of te force of static friction acting on the crate is the horizontal force of 45N since it is less than maximum static friction.