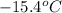Answer : The freezing point of a solution is
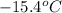
Explanation : Given,
Molal-freezing-point-depression constant
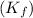 =
=
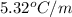
Mass of urea (solute) = 29.82 g
Mass of solvent = 500 g = 0.500 kg
Molar mass of urea = 60.06 g/mole
Formula used :

where,
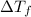 = change in freezing point
= change in freezing point
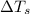 = freezing point of solution = ?
= freezing point of solution = ?
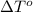 = freezing point of solvent =
= freezing point of solvent =
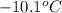
i = Van't Hoff factor = 1 (for urea non-electrolyte)
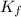 = freezing point constant =
= freezing point constant =
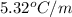
m = molality
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get
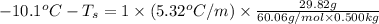
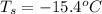
Therefore, the freezing point of a solution is