Answer:
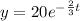
Exponential decay
Explanation:
We are given that
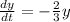
y=20 when t=0
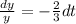
Taking integration on both sides then we get
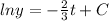
Using formula
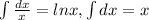
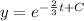
Using formula
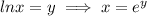
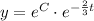
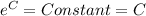
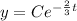
Substitute y=20 and t=0
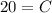
Substitute the value of C
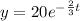
When t tends to infinity then
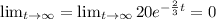
When time increases then the value of function decrease
Hence, the function is exponential decay.