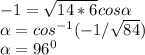Answer:
a.
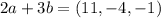
b.
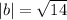 .
.
c.
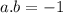
d.
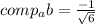
e.
![proj_(a)b= (-1)/(6)[1,1-2]\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/tr2gyc91ivfkq9a2s9ibzilvaujvkrp21g.png)
f.
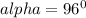
Explanation:
The vector representation of A,B,C is written as
a=[1,1,-2]
b=[3,-2,1]
c=[0,1,-5].
a.To determine the scalar product of 2a+3b we have
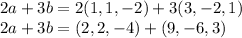
we add component by component w arrive at
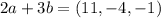
b. we determine the magnitude of vector b i.e |b|. since b=[3,-2,1]
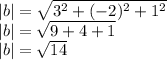 .
.
c.a.b is the dot product of vector a and vector b.
![a.b=[1,1,-2].[3,-2,1]\\a.b=(1*3)+(1*-2)+(-2*1)\\a.b=3-2-2\\a.b=-1](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/d2oc2yzhtwuz5egojrmxkrea9he6x3wlhm.png)
d. to find the component of b on a we use the expression
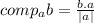
where
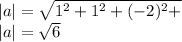
Hence if we substitute values we have
![comp_(a)b=([3,-2,1].[1,1,-2])/(√(6))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/gq53xxguhv1te90htk36zfpdl6jw5cdjod.png)
but earlier a.b=b.a=-1
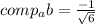
e. to find the projection of b on a we have the expression
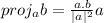
If we substitute values we arrive at
![proj_(a)b= ([3,-2,1].[1,1,-2])/(|a|^(2))a \\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/pbkx9z54gb0yj27ew9twdfwn9emiakv4xf.png)
also recall that earlier we calculated a.b=b.a=-1 and
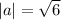
Hence
![proj_(a)b= (-1)/(√(6)^(2))[1,1-2] \\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/syapn4gklovka0rprhfpegpsfcfd3vi2ww.png)
Hence
![proj_(a)b= (-1)/(6)[1,1-2] \\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/uwq116su5qgojlllvfa19zjlq15kdhtam1.png)
f. to determine the angle between vector "a" and "b" we use
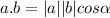
where ∝ is the required angle . If we substitute values into the expression we arrive at