Answer:
CaO is the limiting reagent
Theoritical yield = 25.71 g
% Yield = 75.44%
Step-by-step explanation:
1 mole = Molar mass of the substance
Molar Mass of CaO = 56 g/mol
Molar Mass of CaCO3 = 100 g/mol
Molar mass of CO2 = 44 g/mol
The balanced Equation is :
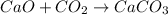
1 mole of CaO reacts with = 1 mole of CO2
56 g of CaO reacts with = 44 g of CO2
1 g of CaO reacts with =
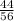
= 0.785 g of CO2
So,
14.4 g of CaO must react with = (14.4 x 0.785) g of CO2
= 11.31 g of CO2
Needed = 11.31 g
Available CO2 = 13.8 g (given)
So CO2 is in excess , hence CaO is the limiting reagent and product will produce from 14.4 g of CaO
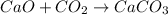
1 mole of CaO will produce 1 mole pf CaCO3
56 g of CaO produce = 100 g of CaCO3
1 g of CaO produce =
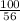
= 1.785 g of CaCO3
14.4 g of CaO will produce = (1.785 x 14.4) g of CaCO3
= 25.71 g of CaCO3
Theoritical Yield of CaCO3 = 25.71 g
Actual yield = 19.4 g
Percent Yield =
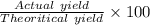
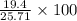
= 75.44 %