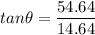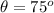Answer:
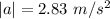
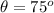
Step-by-step explanation:
Net Force And Acceleration
The Newton's second law relates the net force applied on an object of mass m and the acceleration it aquires by
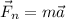
The net force is the vector sum of all forces. In this problem, we are not given the magnitude of each force, only their angles. For the sake of solving the problem and giving a good guide on how to proceed with similar problems, we'll assume both forces have equal magnitudes of F=40 N
The components of the first force are
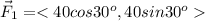
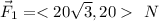
The components of the second force are
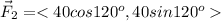
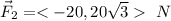
The net force is
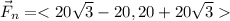
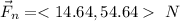
The magnitude of the net force is
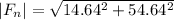
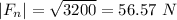
The acceleration has a magnitude of
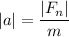
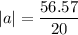
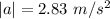
The direction of the acceleration is the same as the net force: