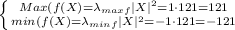Answer:
The absolute maximum of f(x,y) is 121. The absolute minimum of f(x,y) is -121
Explanation:
The given function f(x,y) can be seen as a quadratic form:
^(T)=X^(T)AX](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/x7lgzd2l1duxf8gr5or34udh3xk7o5vjd0.png)
The constraint can be seen as:
^(T)=121\\X^(T)IX=X^(T)X=|X|^2=121](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/guv93pcr6dj1bu1xksqb6cwc5gof3cgbz7.png)
Using the Min-max theorem with Rayleigh–Ritz quotient, we can easly obtain the absolute maximum and minimum of a quadratic form:
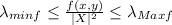
Therefore:
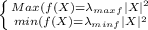
So the problem is reduced to obtain the maximum and minimum eigenvalues of the matrix A.
This eigenvalues can be obtained directly (diagonal matrix), where
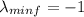 and
and
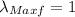 . Therefore:
. Therefore: