Answer: The heat required is 6.88 kJ.
Step-by-step explanation:
The conversions involved in this process are :
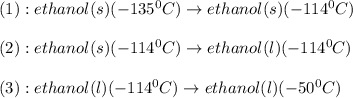
Now we have to calculate the enthalpy change.
![\Delta H=[m* c_(p,s)* (T_(final)-T_(initial))]+n* \Delta H_(fusion)+[m* c_(p,l)* (T_(final)-T_(initial))]+n* \Delta H_(vap)+[m* c_(p,g)* (T_(final)-T_(initial))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/98db46xlz0vae9ufo6b6c9jy8p961nm5mf.png)
where,
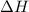 = enthalpy change = ?
= enthalpy change = ?
m = mass of ethanol = 25.0 g
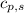 = specific heat of solid ethanol= 0.97 J/gK
= specific heat of solid ethanol= 0.97 J/gK
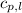 = specific heat of liquid ethanol = 2.31 J/gK
= specific heat of liquid ethanol = 2.31 J/gK
n = number of moles of ethanol =
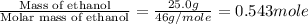
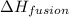 = enthalpy change for fusion = 5.02 KJ/mole = 5020 J/mole
= enthalpy change for fusion = 5.02 KJ/mole = 5020 J/mole
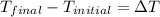 = change in temperature
= change in temperature
The value of change in temperature always same in Kelvin and degree Celsius.
Now put all the given values in the above expression, we get
![\Delta H=[25.0 g* 0.97J/gK* (-114-(-135)K]+0.534mole* 5020J/mole+[25.0g* 2.31J/gK* (-50-(-114))K]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/j2ujz75pnpq7sywt0khf18lwc7225jgei7.png)
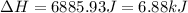 (1 KJ = 1000 J)
(1 KJ = 1000 J)
Therefore, the heat required is 6.88 kJ