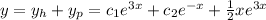Answer:
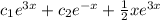
Explanation:
For homogeneous solution:
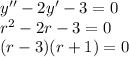
So since roots are r = 3 and r = -1,
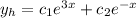
Since we are given
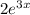 , we will use undetermined coefficients. However, here the trick is we have
, we will use undetermined coefficients. However, here the trick is we have
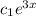 in homogeneous solution. So in particular solution, as undetermined coefficients, we will use
in homogeneous solution. So in particular solution, as undetermined coefficients, we will use
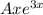 instead of
instead of
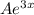 .
.
Hence,
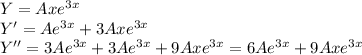
So,
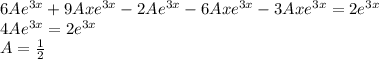
Hence,
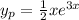
General solution is: