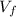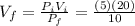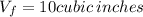Answer:
B.
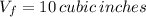
Step-by-step explanation:
Assuming we are dealing with a perfect gas, we should use the perfect gas equation:
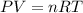
With T the temperature, V the volume, P the pressure, R the perfect gas constant and n the number of mol, we are going to use the subscripts i for the initial state when the gas has 20 cubic inches of volume and absolute pressure of 5 psi, and final state when the gas reaches 10 psi, so we have two equations:
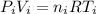 (1)
(1)
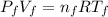 (2)
(2)
Assuming the temperature and the number of moles remain constant (number of moles remain constant if we don't have a leak of gas) we should equate equations (1) and (2) because
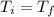 ,
,
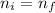 and R is an universal constant:
and R is an universal constant:
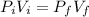 , solving for
, solving for