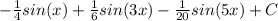Answer:
Explanation:
We begin with the integral
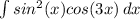
First, we can apply the power reducing formula to
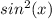
This formula states:
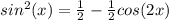
This gives us
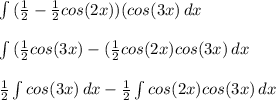
Now, we can use integrate the first integral
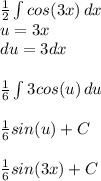
And now we can begin to integrate the second
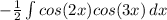
To integrate this, we need to use the Product-to-sum formula, which states
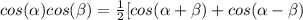 . For this formula, we will use
. For this formula, we will use
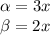
This gives us
![-(1)/(2) \int{(1)/(2)[cos(5x)+cos(x)] } \, dx \\\\-(1)/(4) \int{[cos(5x)+cos(x)] } \, dx\\\\-(1)/(4)\int{cos(5x)} \, dx -(1)/(4)\int{cos(x)} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/rgac9poj83b4dlb3326le4ivrmrx73md5r.png)
We can then use the same process of u-substitution as the previous to get the answer of
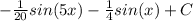
Lastly, we can add the values of the two integrals together to give us the final solution of