Answer: a) 0.5328 b) 0.9772
Explanation:
Given : Resistors to be used in a circuit have average resistance 200 ohms and standard deviation 10 ohms.
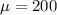 and
and
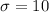
We assume that the resistance in circuits are normally distributed.
a) Let x denotes the average resistance of the circuit.
Sample size : n= 25
Then, the probability that the average resistance for the 25 resistors is between 199 and 202 ohms :-
![P(199<x<200)=P((199-200)/((10)/(√(25)))<(x-\mu)/((\sigma)/(√(n)))<(202-200)/((10)/(√(25))))\\\\=P(-0.5<z<1)\ \ [\because z=(x-\mu)/((\sigma)/(√(n)))]\\\\=P(z<1)-P(z<-0.5)\\\\=P(z<1)-(1-P(z<0.5))\ \ [\because\ P(Z<-z)=1-P(Z<z)]\\\\=0.8413-(1-0.6915)\ \ [\text{By z-table}]\\\\=0.5328](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/7hckbwr1lkqp75s6w96u80kli2yc7gyv9e.png)
b) Total resistors = 25
Let Z be the total resistance of 25 resistors.
To find P(Z≤5100 ohms) , first we find the mean and variance for Z.
Mean= E(Y) = E(25 X)=25 E(X)=25(200)= 5000 ohm
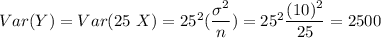
The probability that the total resistance does not exceed 5100 ohms will be :
![P(Y\leq5000)=P((Y-\mu)/(√(Var(Y)))<(5100-5000)/(√(2500)))\\\\=P(z\leq2)=0.9772\ \ [\text{By z-table}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/wvbrodgx6bq5iyaun76u8itf9641gpkrms.png)
Hence, the probability that the total resistance does not exceed 5100 ohms = 0.9772