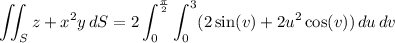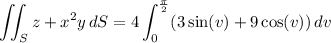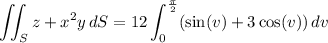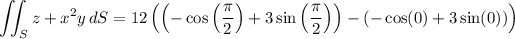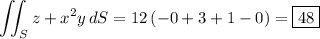Parameterize S in cylindrical coordinates by
s(u, v) = x(u, v) i + y(u, v) j + z(u, v) k
s(u, v) = u i + 2 cos(v) j + 2 sin(v) k
with 0 ≤ u ≤ 3 and 0 ≤ v ≤ π/2.
Take the normal vector to S to be
n = ∂s/∂v × ∂s/∂u
n = 2 cos(v) j + 2 sin(v) k
Then the norm of this vector is
||n|| = √((2 cos(v))² + (2 sin(v))²) = 2
so that the surface element is
dS = ||n|| du dv = 2 du dv
The surface integral is then