Explanation:

Given that lines makes an angle α, β, γ with x - axis, y - axis and z - axis respectively.
So, By definition of direction cosines,
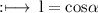
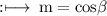
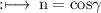
So,
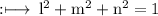
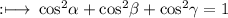
On multiply by 2 on both sides we get
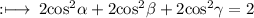
can be further rewritten as
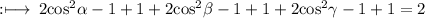
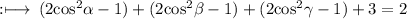
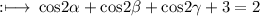
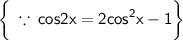
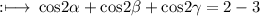
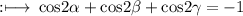
Hence,
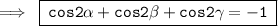
So, option (d) is correct.
▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬▬
MORE TO KNOW
Direction cosines of a line segment is defined as the cosines of the angle which a line makes with the positive direction of respective axis.
The scalar components of unit vector always give direction cosines.
The scalar components of a vector gives direction ratios.