When it comes to right triangles, there's one extremely important equation that you'll have to use almost every single time you come across one: the Pythagorean Theorem.
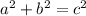 ... Does that equation ring any bells? This equation is utilized to solve for any of the sides of a right triangle, given that you know the values of two of the sides. in a right triangle, there are three sides - one of which is known as a hypotenuse (the longest side of a right triangle). Variables a and b represent the lengths of the non-hypotenuse sides (basically, the two smaller sides, the ones that form a right angle). There's no special rule to which side is designated a and which is designated b, so don't worry about trying to figure out which side should be labeled which. Variable c represents the length of the hypotenuse.
... Does that equation ring any bells? This equation is utilized to solve for any of the sides of a right triangle, given that you know the values of two of the sides. in a right triangle, there are three sides - one of which is known as a hypotenuse (the longest side of a right triangle). Variables a and b represent the lengths of the non-hypotenuse sides (basically, the two smaller sides, the ones that form a right angle). There's no special rule to which side is designated a and which is designated b, so don't worry about trying to figure out which side should be labeled which. Variable c represents the length of the hypotenuse.
Now, how can we apply the Pythagorean Theorem to this question? We are given the values of the two legs of the triangle, 1 m and
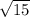 m. Since we are prompted to solve for the length of the hypotenuse, we will use the Pythagorean Theorem and solve for c, the variable for the length of the hypotenuse.
m. Since we are prompted to solve for the length of the hypotenuse, we will use the Pythagorean Theorem and solve for c, the variable for the length of the hypotenuse.
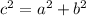
c =
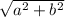
(We square root both sides in order to isolate c. Now, let's plug in the values we were given. As we learned earlier, it doesn't matter which leg is a or b)
c =
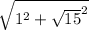
c =
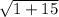
c =
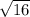
c = 4 (m)
The length of the hypotenuse is 4 meters.
And we're done! Though I wrote a lot, the equation is fairly simple and will come extremely handy any time you're faced with questions like these. If you have any questions about anything I wrote here or you need clarification on anything, let me know!
- breezy ツ