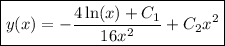Use reduction of order. Given a solution
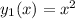 , look for a second solution of the form
, look for a second solution of the form
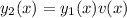 .
.
Compute the first two derivatives of
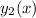 :
:
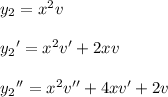
Substitute them into the ODE:
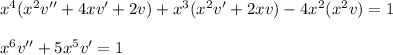
Now substitute
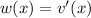 and you end up with a linear ODE:
and you end up with a linear ODE:
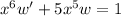
Multiply through both sides by
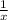 (if you're familiar with the integrating factor method, this is it):
(if you're familiar with the integrating factor method, this is it):
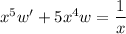
Bear in mind that in order to do this, we require
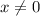 . Just to avoid having to deal with absolute values later, let's further assume
. Just to avoid having to deal with absolute values later, let's further assume
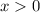 .
.
Notice that the left side is the derivative of a product,
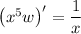
Integrate both sides with respect to
 :
:
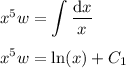
Solve for
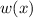 :
:
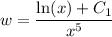
Solve for
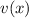 by integrating both sides:
by integrating both sides:
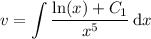
Integrate by parts:
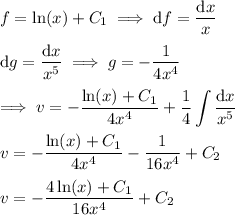
Solve for
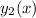 :
:
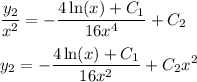
But since
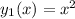 is already accounted for, the second solution is just
is already accounted for, the second solution is just
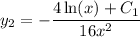
Still, the general solution would be